 What is Computer Access? When we talk about computers we are referring to hardware and software products that enable people with disabilities to access, interact with, and use computers. Assistive devices in this category includes modified or alternate keyboards, input and pointing devices such as large “mice” or switches activated by pressure or some other means, and software including speech-to-text software. Even if the device is a “generic” product (e.g. a “vertical” mouse or large trackball), the product is considered assistive technology if it is needed by someone with a disability. Computer operating systems now come with many “built in” accessibility features that may provide sufficient support when “turned on” and customized for the user.
What is Computer Access? When we talk about computers we are referring to hardware and software products that enable people with disabilities to access, interact with, and use computers. Assistive devices in this category includes modified or alternate keyboards, input and pointing devices such as large “mice” or switches activated by pressure or some other means, and software including speech-to-text software. Even if the device is a “generic” product (e.g. a “vertical” mouse or large trackball), the product is considered assistive technology if it is needed by someone with a disability. Computer operating systems now come with many “built in” accessibility features that may provide sufficient support when “turned on” and customized for the user.
When do I need to use AT for Computer Access? AT may be needed at any time and in many places. Whether in school, work, or in the community, computer use is important in all areas of our lives.
Who needs Computer Access AT? Anyone struggling with the three functional barriers: 1) providing computer input 2) interpreting output, and 3) reading supporting documentation. Individuals with motor, sensory, cognitive or learning disabilities all can benefit from assistive technology options.
Why aren’t computers more accessible? Too often, people think of accessibility as an add-on to a device or program. Increasingly today, developers and designers are realizing that maintenance becomes easier when accessibility is part of the basic design. Now, many smartphones, tablets and computers also include screen readers, word prediction and speech recognition.
Solutions for Computer Access Needs
The links to solutions below are intended as examples only to give you an idea of the types of AT available. You may find more examples in the Resources section or by viewing the devices available for loan on the website of your state or territory AT program.
Resources for Computer Access
Information on this page addresses Assistive Technology for people who have difficulty interacting with a computer
because of sensory, motor, or cognitive limitations in...
EDUCATION | EMPLOYMENT | COMMUNITY LIVING
(click the titles above to jump to the content area)
EDUCATION
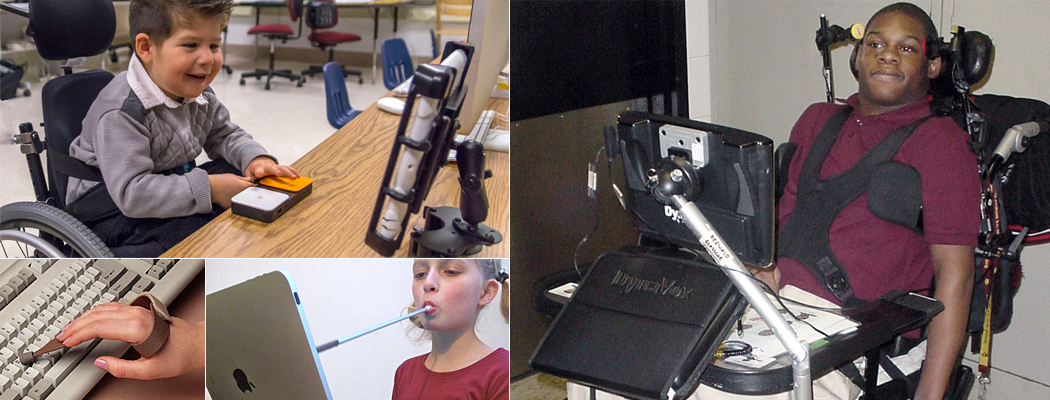

Talking Points for Computer Access Assistive Technology in Education
The category of Education encompasses learners - young and old - who are participating as a student whether at the pre-school, elementary, middle/junior or high school levels. It also refers to those attending post-secondary institutions, vocational training programs, and adult education classes.
For children transitioning into the public school at age 3 - To ensure successful AT transitions for children turning 3 years old, it is important for any AT the child is currently using or may need to use in school, whether written into the child's Individualized Family Service Plan (IFSP) or not, be incorporated into the child's Individualized Education Program (IEP).
For students transitioning into the community or employment settings upon high school graduation - To ensure successful AT transitions for students aging out of school services, it is important for any AT the student is currently using or may need to pursue employment outcomes, whether written into the child's Individualized Education Program (IEP) or not, be incorporated into the student's Individualized Plan for Employment (IPE). IPEs are developed through collaboration with your state vocational rehabilitation agency using a Vocational Rehabilitation (VR) Counselor.
For students transitioning into college or other higher education programs - Students transitioning out of high school into college or other higher education institutions should explore AT needs in advance of enrolling in classes. Meeting with the school's student disability services office is one key element in anticipating issues and exploring situations.
Situations Where a Student Might Need Assistive Technology for Computer Access:
Students may need computer access within the classroom where instruction occurs, as well as at home (for homework and when “school” is home-schooling, cyber-school, or on-line courses). They may also need computer access at sites that are providing internships or community-based instruction, or community resources needed to complete educational assignments (e.g. public library). What are examples of tasks or activities for which a student needs Computer Access AT?
- Notetaking
- Writing
- Reading
- Calculating
- Organizing and planning
- Test taking (including standardized and state testing
Commonly Asked Questions for a Student Who Needs Computer Access AT
Please listen to this section and/or download a transcript. TXT
Talking Points for Computer Access Assistive Technology in Employment
The category of Employment encompasses those people of working-age who are currently employed or who are seeking employment. It can also include those who are participating in a work experience (i.e., internships, volunteer work, etc.)
For individuals transitioning into employment settings upon high school graduation - To ensure successful AT transitions for students aging out of school services, it is important to have access to any AT needed to pursue employment outcomes including in the application process. One option may be to investigate your state's vocational rehabilitation agency to develop an Individualized Plan for Employment (IPE) which should include any needed AT.
Situations where an Individual might need Assistive Technology for Computer Access
Work Environment
- Interview process
- Meetings
- Trainings
- Daily tasks
- Telecommunications
- Group and Committee Activities
Socialization
- Work lunches
- Social media
- Employer sponsored events
Home & Community Environment
- Preparing for work
Community
- Library
- Shopping for essentials
- Employment-related transportation
- Employment-related public events
Commonly Asked Questions for an Individual Who Has Computer Access Needs in Employment
Q - Where can I obtain more information and/or try some computer access options?
A - You can contact your State Assistive Technology Program who can provide information and assistance, an interactive demonstration of available options and the opportunity to borrow a device so you “try before you buy.” These services are usually free of charge. To find your state program go to Find Your State Program.
Q - When can I ask for an assistive device to be used for employment purposes?
A - Federal legislation ensures the right to reasonable accommodations including the use of assistive technology for qualified individuals at all stages of employment including the application and interview process. You can obtain more information through the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) website, https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/types/disability.cfm
Talking Points for Assistive Technology for Computer Access in Community Living
The category of Community Living encompasses carrying out daily activities, participating in community activities (e.g., social and recreational activities), using community services (e.g., public transportation and libraries) and living independently. The category is applicable to individuals with disabilities as well as family members and others providing support and care. When options are needed to increase independent functioning and participation, there are a variety of possible AT solutions. Regardless of age, the ability to use a computer for tasks and to access the Internet, email and social media is more important than ever.
Situations where an individual might need assistive technology for Computer Access
Community
- Doctor's office visits
- Hospital
- Shopping
- Transportation to, and from, events
- Entertainment
- Library
Family/Home Environment
- Talking on the phone
- Paying bills
- TV/Radio
- Computer tasks/games

 She cannot access the keyboard on the computer like her peers. She has tried various adapted mice, alternative keyboards and switches. She enjoys playing on the computer and looks forward to computer time every day.
She cannot access the keyboard on the computer like her peers. She has tried various adapted mice, alternative keyboards and switches. She enjoys playing on the computer and looks forward to computer time every day.

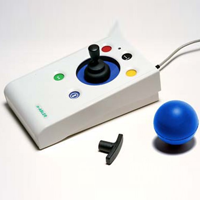
 This student is in 6th grade, 12 years old, and struggles with fine motor control. He cannot write with a regular pencil. He has tried various pencil grips and other alternatives. He is able to do some things with his hands such as pushing larger buttons, and he truly enjoys working on the computer.
This student is in 6th grade, 12 years old, and struggles with fine motor control. He cannot write with a regular pencil. He has tried various pencil grips and other alternatives. He is able to do some things with his hands such as pushing larger buttons, and he truly enjoys working on the computer.

 This student is a senior in high school, 17 years old and survived a skiing accident but broke his third and fourth vertebrae. He is now confined to a wheelchair as a quadriplegic. He has retained good head and trunk control and can move his right arm minimally from the shoulder. He has good movement in his thumb, index finger and second finger of his right hand. He is very motivated to complete his regular high school program and get back to his after school job.
This student is a senior in high school, 17 years old and survived a skiing accident but broke his third and fourth vertebrae. He is now confined to a wheelchair as a quadriplegic. He has retained good head and trunk control and can move his right arm minimally from the shoulder. He has good movement in his thumb, index finger and second finger of his right hand. He is very motivated to complete his regular high school program and get back to his after school job.
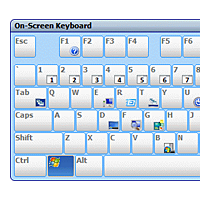


 She cannot access any form of tablet or computer. She is extremely smart and wants to play on her mother’s iPad.
She cannot access any form of tablet or computer. She is extremely smart and wants to play on her mother’s iPad.


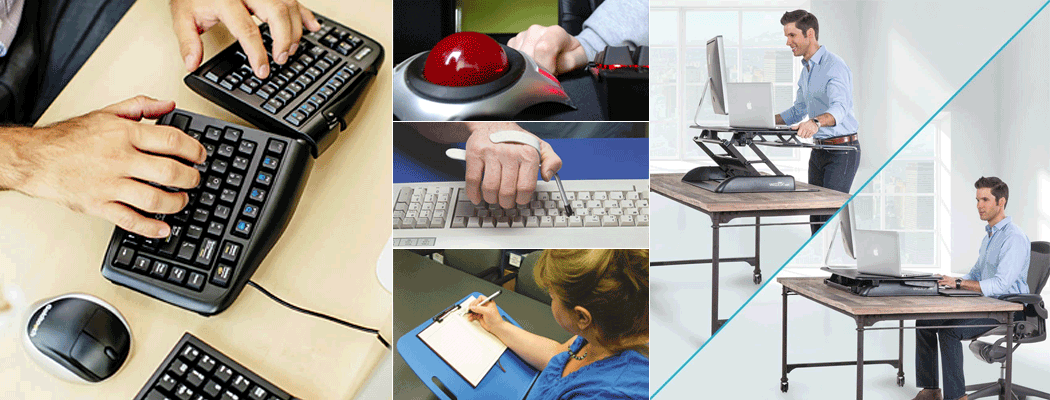
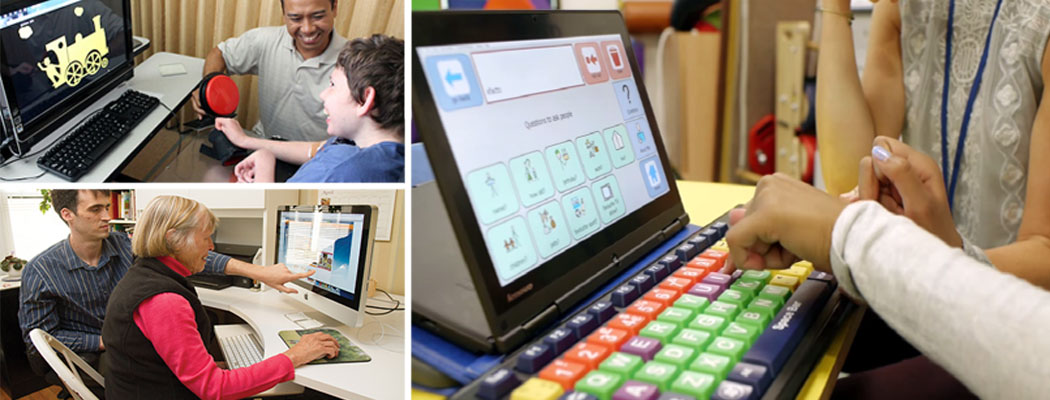
 Possible Recommendations:
Possible Recommendations:





